[Data Structure] 스택 - 중위표기수식 -> 후위표기수식
2021. 12. 2. 20:20ㆍMajor`/자료구조
※ 연산자 우선순위 : ( ) < +, - < ×, /
알고리즘
- 연산자를 잠시 stack에 저장
- if) 다음 처리할 연산자 우선순위 < stack에 존재하는 연산자 우선순위
- -> stack에 존재하는 연산자 pop한 후, 다음 처리 연산자 push
- 왼쪽 괄호 -> 오른쪽 괄호 만날때 까지, 왼쪽 괄호위에 push된 연산자 pop
int priority(char op) { // 연산자 우선순위
switch (op) {
case '(': case')':
return 1;
case '+': case'-':
return 2;
case '*': case'/':
return 3;
}
return -1;
}
void infix_to_postfix(const char* str) {
stack s;
init_stack(&s);
int len = strlen(str);
char ch, top_stack; // top_stack = 스택의 가장 위에 있는 연산자
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ch = str[i];
switch (ch) {
case '+': case'-': case'*': case'/':
// 다음 연산자 우선순위 <= stack에 존재하는 연산자 우선순위 -> stack pop시키고 다음 연산자 push
while (!is_empty(&s) && (priority(ch) <= priority(peek(&s))))
printf("%c", pop(&s));
push(&s, ch);
break;
case '(':
push(&s, ch);
break;
case ')':
top_stack = pop(&s); // stack top에 있는 연산자 pop해서 확인
while (top_stack != '(') {
// 다음 연산자가 ')'이면 '('를 만날때까지 그외의 연산자는 pop시켜서 return
printf("%c", top_stack);
top_stack = pop(&s);
}
break;
default: // 피연산자
printf("%c", ch);
break;
}
}
while (!is_empty(&s)) // stack이 다 비워지지않음 = stack안에 아직 연산자가 남아있음 -> 전부 return
printf("%c", pop(&s));
}
※ Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100
typedef char element;
typedef struct {
int top;
element stack[MAX_STACK_SIZE];
}stack;
void init_stack(stack* s) {
s->top = -1;
}
int is_full(stack* s) {
return s->top == MAX_STACK_SIZE - 1;
}
int is_empty(stack* s) {
return s->top ==-1;
}
void push(stack* s, element item) {
if (is_full(s)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Stack is full!!");
return;
}
else
s->stack[++(s->top)] = item;
}
element pop(stack* s) {
if (is_empty(s)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Stack is empty!!");
return;
}
else
return s->stack[(s->top)--];
}
element peek(stack* s) {
if (is_empty(s)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Stack is empty!!");
return;
}
else
return s->stack[s->top];
}
int priority(char op) { // 연산자 우선순위
switch (op) {
case '(': case')':
return 1;
case '+': case'-':
return 2;
case '*': case'/':
return 3;
}
return -1;
}
void infix_to_postfix(const char* str) {
stack s;
init_stack(&s);
int len = strlen(str);
char ch, top_stack; // top_stack = 스택의 가장 위에 있는 아이템
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ch = str[i];
switch (ch) {
case '+': case'-': case'*': case'/':
// 이제 들어갈 연산자 우선순위 <= stack에 존재하는 연산자 우선순위 -> stack pop시키고 처리할 연산자 push
while (!is_empty(&s) && (priority(ch) <= priority(peek(&s))))
printf("%c", pop(&s));
push(&s, ch);
break;
case '(':
push(&s, ch);
break;
case ')':
top_stack = pop(&s); // stack top에 있는 연산자 pop해서 확인
while (top_stack != '(') {
// 다음 연산자가 ')'이면 '('를 만날때까지 그외의 연산자는 pop시켜서 return
printf("%c", top_stack);
top_stack = pop(&s);
}
break;
default: // 피연산자
printf("%c", ch);
break;
}
}
while (!is_empty(&s)) // stack이 다 비워지지않음 = stack안에 아직 연산자가 남아있음 -> 전부 return
printf("%c", pop(&s));
}
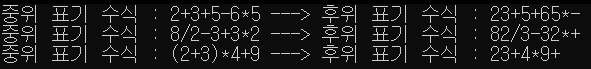
int main(void) {
char * str1 = "2+3+5-6*5";
char* str2 = "8/2-3+3*2";
char* str3 = "(2+3)*4+9";
printf("중위 표기 수식 : %s ---> 후위 표기 수식 : ", str1);
infix_to_postfix(str1);
printf("\n");
printf("중위 표기 수식 : %s ---> 후위 표기 수식 : ", str2);
infix_to_postfix(str2);
printf("\n");
printf("중위 표기 수식 : %s ---> 후위 표기 수식 : ", str3);
infix_to_postfix(str3);
printf("\n");
}