[Data Structure] 히프 정렬 - Heap Sort
2022. 1. 1. 14:47ㆍMajor`/자료구조
히프 정렬 (Heap Sort)

Unstable Sort
- 완전이진트리 구조
- 배열을 이용해서 구현 or 컬렉션을 통해서 구현
시간복잡도
- O(n log n)
장점
- 추가 메모리가 필요없고 항상 O(n log n)의 시간복잡도를 가진다
단점
- 보통의 경우, 퀵정렬보다 느리다
- 데이터의 상태에 따라서 다른 정렬들에 비해 조금 느리다
- 안정성을 보장받지 못한다
과정
- 최대힙 : 힙에서 pop시킨 요소를 배열의 뒤에서부터 채운다
- 최소힙 : 힙에서 pop시킨 요소를 배열의 앞에서부터 채운다
- C : 직접 구현
- Java : PriorityQueue / 직접 구현
- Python : heapq / PriorityQueue / 직접 구현
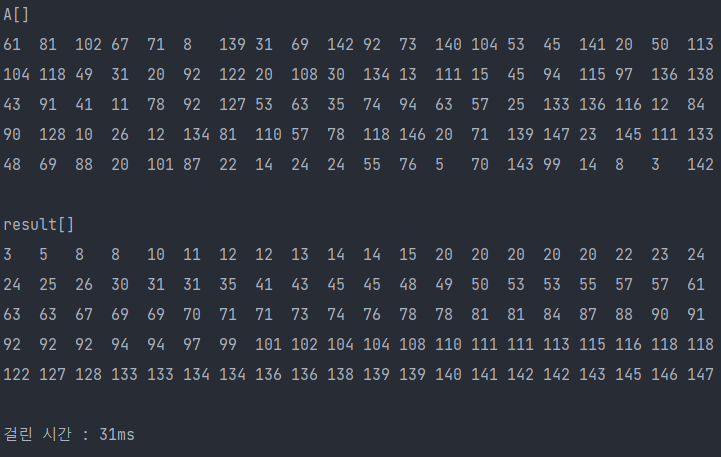
▶ PriorityQueue 이용
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq1 = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 최소 힙
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); // 최대 힙
static void min_heap(int[]A1, PriorityQueue<Integer> pq1){
for(int i=0; i<A1.length; i++)
A1[i] = pq1.poll();
}
static void max_heap(int[]A2, PriorityQueue<Integer> pq2){
for(int i=A2.length-1; i>=0; i--)
A2[i] = pq2.poll();
}
▶ 직접 Heap 구현
class Heap{
private int maxsize, heap_size;
private int [] heap;
Heap(int maxsize){
this.maxsize = maxsize;
this.heap_size = 0;
heap = new int[maxsize];
}
boolean is_full(){
return heap_size == maxsize;
}
boolean is_empty(){
return heap_size == 0;
}
void insert(int num){
if(is_full()) return;
else{
int index = ++heap_size;
while(index != 1 && (num > heap[index/2])){
heap[index] = heap[index/2];
index/=2;
}
heap[index] = num;
}
}
int delete(){
if(is_empty()) return 0;
else{
int root = heap[1];
int last = heap[heap_size--];
int index = 1;
int child = 2;
while(child<=heap_size){
if((child<heap_size) && (heap[child] < heap[child+1]))
child++;
if(last>=heap[child]) break;
heap[index] = heap[child];
index = child;
child*=2;
}
heap[index] = last;
return root;
}
}
}
static void heap_sort(Heap heap, int[] result){
for(int i=result.length-1; i>=0; i--)
result[i] = heap.delete();
}
▶ PriorityQueue 결과
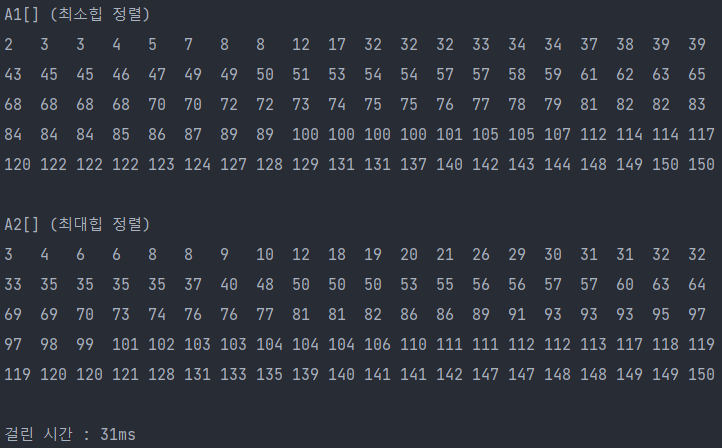
▶ 직접 Heap 구현 결과