[Data Structure] 우선순위 큐 (히프)
2021. 12. 18. 16:49ㆍMajor`/자료구조
728x90
반응형
우선순위 큐 (priority queue)
- 일반적인 큐 : FIFO(First In First Out)구조
- 우선순위 큐 : 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나간다
- 시뮬레이션 시스템, 네트워크 트래픽 제어, 작업 스케쥴링, 수치해석계산 등에 사용
| 자료구조 | 삭제되는 요소 |
| Stack | 가장 늦게 들어온 데이터 (LIFO) |
| Queue | 가장 먼저 들어온 데이터 (FIFO) |
| Priority Queue | 가장 우선순위가 높은 데이터 (Priority) |
구현 방법
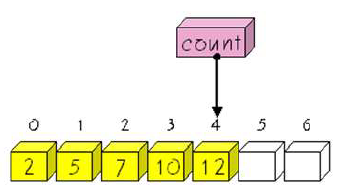
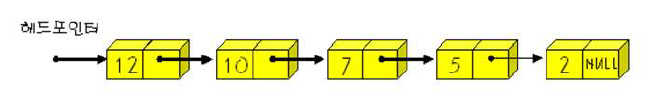

- 배열 / 연결리스트 / 히프
| 표현 방법 | 삽입 | 삭제 |
| 정렬 안된 배열/연결 리스트 | O(1) | O(n) |
| 정렬 된 배열/연결 리스트 | O(n) | O(1) |
| 힙 | O(log n) | O(log n) |
- 만약 n이 1000일 경우
- O(n) : 1000초 / O(log₂n) : 10초
∴ 힙의 효율은 배열/연결 리스트보다 훨씬 좋다
힙 (Heap)
- 완전 이진 트리 기반
- 배열을 이용해서 구현
- 여러 개의 값들 중에 max, min을 빠르게 찾아내도록 설계된 자료구조
- 힙트리는 이진탐색트리와 달리, 중복된 값을 허용한다
- 힙 안에서 데이터들은 느슨한 정렬 상태를 유지
- 힙의 목적 : delete 연산 시, 가장 큰 값 찾아내기 → 전체를 정렬할 필요가 없다
힙의 종류
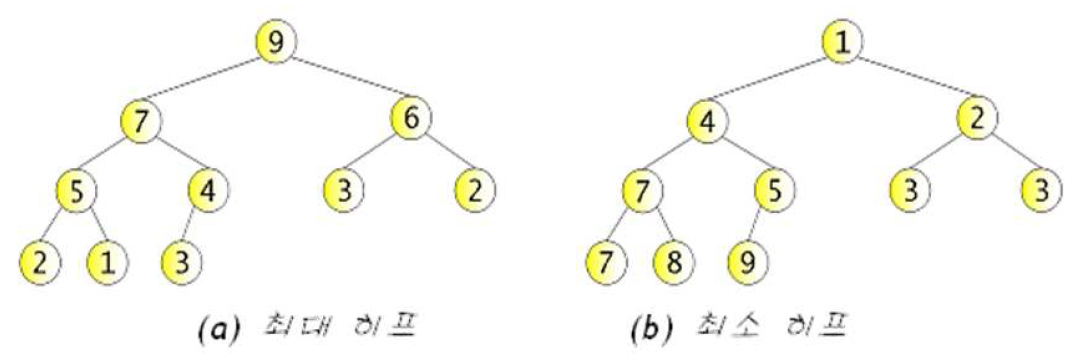
▶ 최대 힙
- key(부모 노드) ≥ key(자식 노드)
▶ 최소 힙
- key(부모 노드) ≤ key(자식 노드)
힙 구현 (최대 힙)

- 각 노드(레벨 별로) 번호 부여 (루트 노드 = 1)
- 각각의 번호를 배열의 인덱스라고 설정하고 구현
※ 인덱스 (부모↔자식)
- 왼쪽 자식 인덱스 = (부모 인덱스)×2
- 오른쪽 자식 인덱스 = (부모 인덱스)×2 + 1
- 부모 인덱스 = (자식 인덱스)/2
1. 삽입 연산
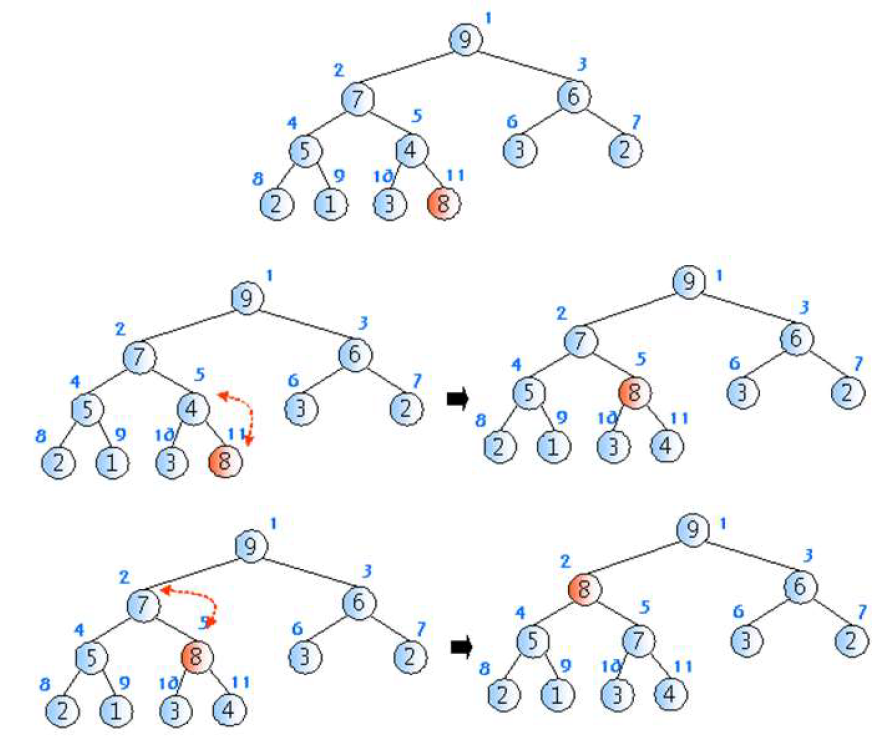
1. item이 들어갈 인덱스 = 현재 히프트리에 있는 최종 item 인덱스의 다음 인덱스
2. 만약, item이 해당 item의 부모 item보다 크면 (item > item의 부모 item)
- item이 들어갈 인덱스(i)에 부모 item을 할당 -- (1)
- item이 들어갈 인덱스(i)를 부모 인덱스로 update : (i/2) -- (2)
- item 인덱스(i)가 해당 인덱스의 부모 인덱스보다 작아질 때 까지 (1), (2) 반복
void insert_node(heapnode* h, element item) {
if (is_full(h)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Heap is full\n\n");
return;
}
else {
int i; // item의 인덱스
i = ++h->heap_size;
// item인덱스 = 현재 히프트리에 있는 최종 item 인덱스의 다음 인덱스
while (i != 1 && (item > h->heap[i / 2])) {
h->heap[i] = h->heap[i / 2];
i /= 2;
}
h->heap[i] = item;
}
}
2. 삭제 연산
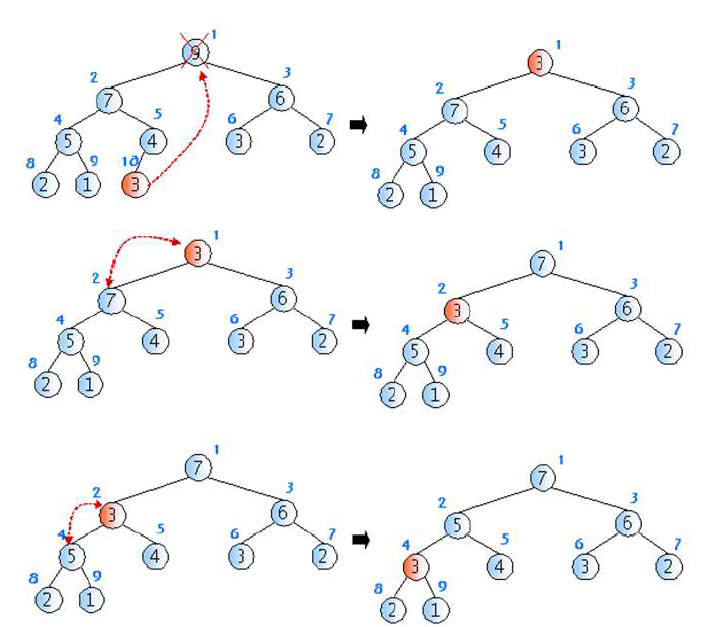
1. 루트 노드를 삭제시키고, 말단 노드를 루트도 옮기기 (루트에 말단 노드의 item 저장)
2. root의 자식들과 root의 값을 비교해서 -- (1)
- root 값 < root자식들 값 : 자식들 중 큰 값을 선택해서 root노드와 교체 -- (2)
- root값 > root 자식들 값이 될 때 까지 (1), (2) 반복
element delete_node(heapnode* h) {
if (is_empty(h)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Heap is empty\n\n");
return;
}
else {
element root = h->heap[1]; // 루트 노드 item
element last = h->heap[h->heap_size--]; // 말단 노드 item
// 루트 노드를 삭제시키고 말단을 루트로 올릴거기 때문에 heap_size는 1 감소
int index = 1; // 말단 노드가 들어가는 index -> 자리 찾을 때 까지 계속 변함
int child = 2;
while (child <= h->heap_size) {
if ((child < h->heap_size) && (h->heap[child] < h->heap[child + 1]))
child++; // 자식 노드 중 더 큰 값의 인덱스 찾기
if (last >= h->heap[child]) break;
// 최종 insert 노드의 값이 해당 인덱스의 자식 값보다 크면 더 이상 옮기기 X
h->heap[index] = h->heap[child];
index = child;
child *= 2;
}
h->heap[index] = last;
return root;
}
}
3. Full Code (Heap)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <ctype.h>
// 배열로 히프 구현
#define MAX_HEAP_SIZE 100
// 밑이 2인 로그함수
double logB(int x, int base) {
return (double)log(x) / log(base);
}
typedef int element; // heap의 요소 type
typedef struct headnode {
int heap_size;
element heap[MAX_HEAP_SIZE];
}heapnode;
heapnode* create() {
return (heapnode*)malloc(sizeof(heapnode));
}
void init_heap(heapnode* h) {
h->heap_size = 0;
}
int heap_length(heapnode* h) {
// heap에 있는 item 개수
return h->heap_size;
}
int is_empty(heapnode* h) {
return h->heap_size == 0;
}
int is_full(heapnode* h) {
return h->heap_size == MAX_HEAP_SIZE - 1;
}
void insert_node(heapnode* h, element item) {
if (is_full(h)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Heap is full\n\n");
return;
}
else {
int i; // item의 인덱스
i = ++h->heap_size;
// item인덱스 = 현재 히프트리에 있는 최종 item 인덱스의 다음 인덱스
while (i != 1 && (item > h->heap[i / 2])) {
h->heap[i] = h->heap[i / 2];
i /= 2;
}
h->heap[i] = item;
}
}
element delete_node(heapnode* h) {
if (is_empty(h)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Heap is empty\n\n");
return;
}
else {
element root = h->heap[1]; // 루트 노드 item
element last = h->heap[h->heap_size--]; // 말단 노드 item
// 루트 노드를 삭제시키고 말단을 루트로 올릴거기 때문에 heap_size는 1 감소
int index = 1; // 말단 노드가 들어가는 index -> 자리 찾을 때 까지 계속 변함
int child = 2;
while (child <= h->heap_size) {
if ((child < h->heap_size) && (h->heap[child] < h->heap[child + 1]))
child++; // 자식 노드 중 더 큰 값의 인덱스 찾기
if (last >= h->heap[child]) break;
// 최종 insert 노드의 값이 해당 인덱스의 자식 값보다 크면 더 이상 옮기기 X
h->heap[index] = h->heap[child];
index = child;
child *= 2;
}
h->heap[index] = last;
return root;
}
}
void clear(heapnode* h) {
h->heap_size = 0;
}
void print_heap(heapnode* h) {
if (is_empty(h)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error : Heap is empty\n\n");
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= heap_length(h); i++) {
printf("[%d] ", h->heap[i]);
if (logB(i + 1, 2) - (int)logB(i + 1, 2) == 0) {
// 1 2 4 8,.. 2의 제곱 때마다 개행
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int main(void) {
heapnode* h;
h = create();
init_heap(h);
print_heap(h);
printf(">> 1~6을 Heap_Tree에 insert\n");
for (int i = 1; i <=6; i++)
insert_node(h, i);
print_heap(h);
printf(">> 10 insert\n"); insert_node(h, 10); print_heap(h);
printf(">> 2 insert\n"); insert_node(h, 2); print_heap(h);
printf(">> 9 insert\n"); insert_node(h, 9); print_heap(h);
printf(">> delete()\n>> delete된 값 : %d\n", delete_node(h)); print_heap(h);
printf(">> delete()\n>> delete된 값 : %d\n", delete_node(h)); print_heap(h);
printf(">> Heap_Tree clear()\n"); clear(h); print_heap(h);
printf(">> 10 insert\n"); insert_node(h, 10); print_heap(h);
printf(">> 2 insert\n"); insert_node(h, 2); print_heap(h);
printf(">> 9 insert\n"); insert_node(h, 9); print_heap(h);
}
728x90
반응형
